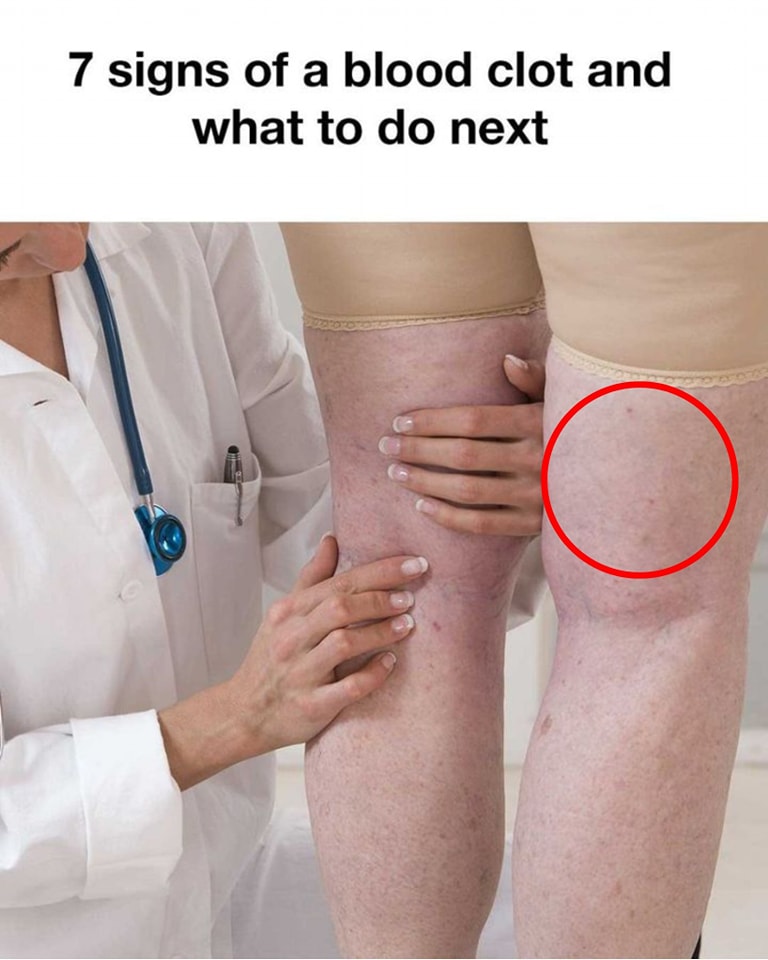
Blood clots are a serious health concern that can lead to dangerous complications if not detected early. It’s crucial to understand what a blood clot feels like so that you can seek timely treatment. In this article, we’ll explore common signs and symptoms of blood clots, helping you recognize the warning signs before they become a life-threatening situation.
Understanding Blood Clots and Their Risks
Blood clots are formed when blood thickens and clumps together to stop bleeding after an injury. However, in some cases, blood clots can form in the veins or arteries without any apparent injury. These abnormal clots can travel to critical areas of the body, such as the lungs (causing a pulmonary embolism), brain (leading to a stroke), or heart (resulting in a heart attack).
Though blood clots can form anywhere in the body, they most commonly occur in the legs (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT). Identifying blood clots early can save lives, which is why it’s important to recognize the signs that something may be wrong.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Blood Clots
1. Swelling in the Affected Area
One of the most common signs of a blood clot is swelling, particularly in the legs or arms. If you notice one limb suddenly swelling up, it could be a sign that a clot is blocking blood flow. The swelling may be accompanied by redness and warmth, especially around the clot.
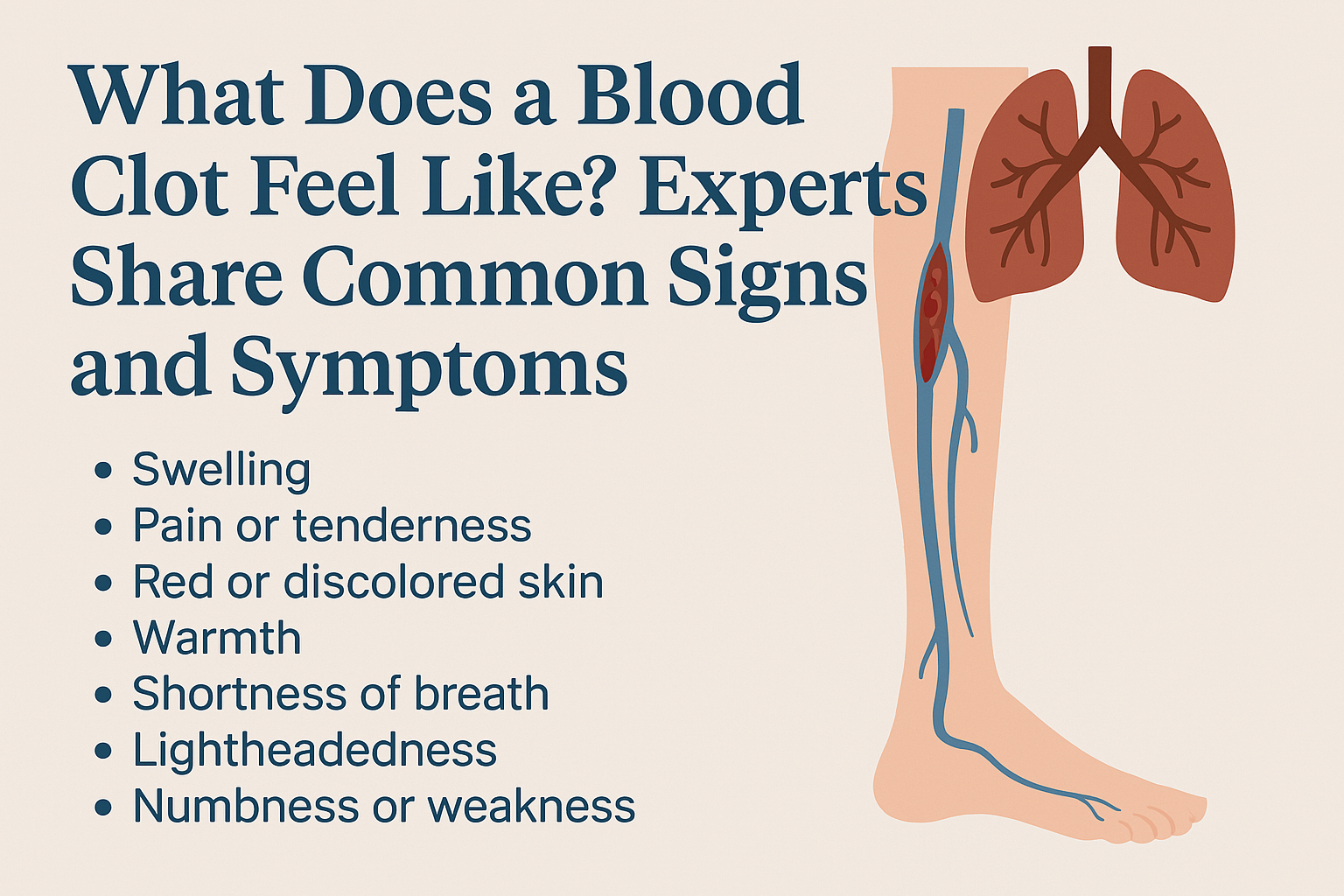
2. Pain or Tenderness
Blood clots often cause discomfort or pain in the affected area. You might experience aching, throbbing, or sharp pain, which may worsen when standing or walking. In cases of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), the pain is often felt in the calf, and it may feel similar to cramping or muscle soreness.
3. Red or Discolored Skin
The skin over a blood clot may appear red or have a bluish tint. If you experience any unusual color changes in the skin along with pain or swelling, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider immediately. Skin discoloration could indicate a blood clot blocking blood flow to the area.
4. Warmth in the Affected Area
Along with swelling and pain, blood clots can cause a feeling of warmth in the affected area. If you touch the area with the clot, you might notice that it feels warmer than other parts of your body. This warmth is due to inflammation caused by the clot blocking normal circulation.
5. Shortness of Breath and Chest Pain
If a blood clot moves to the lungs (pulmonary embolism), it can cause symptoms such as sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and dizziness. This is a medical emergency, and you should seek immediate help. In many cases, pulmonary embolism is life-threatening and requires urgent medical intervention.
6. Lightheadedness or Fainting
Blood clots affecting the lungs, heart, or brain can lead to severe symptoms like dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting. If a clot is blocking blood flow to vital organs, it can disrupt normal circulation, leading to a feeling of being faint or weak.
7. Numbness or Weakness
In the case of a clot affecting the brain (stroke), you might experience sudden numbness or weakness on one side of the body, slurred speech, or difficulty seeing in one or both eyes. If these symptoms occur suddenly, it’s crucial to get medical help immediately.
Risk Factors for Blood Clots
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing a blood clot. These include:
- Prolonged immobility: Sitting for long periods, such as during long flights or bed rest, can lead to blood clots.
- Recent surgery: Surgery, especially orthopedic procedures like hip or knee replacement, can increase the risk of clot formation.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women are at a higher risk due to hormonal changes and the increased pressure on veins.
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to poor circulation, increasing the risk of clots.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of clot formation.
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions like cancer, heart disease, or a history of blood clots can elevate the risk.
How to Prevent Blood Clots
Preventing blood clots starts with managing risk factors. Here are a few tips to help reduce your chances of developing a clot:
- Stay active: Regular exercise and movement help improve circulation and prevent clot formation.
- Maintain a healthy weight: A balanced diet and regular exercise can help you manage your weight and reduce clot risk.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can increase the risk of blood clots. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Avoid smoking: Quitting smoking improves blood circulation and lowers the risk of developing blood clots.
- Wear compression stockings: These can help promote circulation in the legs and reduce the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
What to Do if You Suspect a Blood Clot
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider immediately. Blood clots are serious, and timely treatment can prevent life-threatening complications. Your doctor will perform tests such as ultrasound or blood work to diagnose the presence of a clot and determine the appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Blood clots are a serious health concern, and recognizing the symptoms early can make a significant difference in outcomes. If you experience swelling, pain, or shortness of breath, don’t ignore these signs—seek medical attention right away. By staying informed and taking steps to reduce your risk, you can protect yourself from the dangers of blood clots.
Related Articles:
- Full Story: 10 Signs You’re Eating Too Much Sugar
- 7 Words Depressed People Use More Often: How to Recognize the Signs and Offer Support
- Man Over 700 Eggs in One Month: A Surprising Experiment and Its Impact on the Body
- 20 Early Signs Your Body May Be Fighting Cancer: Understanding the Signals for Better Health
- 12 Health Benefits of Ginger: From Nausea Relief to Reducing Inflammation and More
- Potato Gel for Glowing Skin & Dark Spots
- What Happens to Your Body When You Drink Lemon Water With Turmeric Every Day?
- Why You Should Never Pour Hot Water Into the Sink: A Costly Mistake
- Surprising Effects of Sleeping Without Clothes: Why You Should Try It